The electric vehicle (EV) industry is a rapidly growing industry with immense potential. Despite being a relatively new industry, it has already seen considerable growth and investment. We expect the sector to continue thriving in the coming years as the public becomes aware of the benefits of electric vehicles.
As a leading supplier of low-voltage cables, medium-voltage cables, control cables, fiber optic cables, transformers, switchgears, panelboards, accessories and more. AWG is well-positioned to advance grid modernization for the EV infrastructure sector. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, so does the energy demand.
Shifting Market Demands: A Need for Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
Only 10% of Americans have quick access to an EV charging station. Though EV charging is easily accessible to homeowners via a garage power pack, homeowners, or renters without access to a personal, powerful charging outlet have difficulties locating a public charging station for regular and dependable use.
In the United States, there is a target to have EVs account for half of all new auto sales by 2030, necessitating more consumer incentives. However, if EVs are widely adopted, people must also have easily accessible and reliable charging stations.
In June 2022, the United States Department of Transportation (DOT) issued a notice of proposed rule-making outlining minimum requirements for a federally funded EV charging system that aims to provide a consistent customer experience and pave the way for greater EV adoption. Part of the proposal includes standardized plugs, minimum uptimes, American-made EV chargers, data-sharing provisions, and the capacity for DC fast chargers with the capacity to charge at least four EVs simultaneously at 150 kW or more.
The Impact of the IIJA and IRA
The increasing demand for EV charging infrastructure is bolstered by the movement to reduce carbon emissions. In 2022, the U.S. government passed two acts that support the movement toward clean transportation technologies: the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA).
Investing approximately $370 billion towards climate change mitigation and carbon reduction, the IRA incentivizes businesses to begin investing in medium- and heavy-duty EVs and new chargers with significant tax breaks. The act also offers a $7,500 credit to those with light-duty and passenger EVs.
The white house’s economic plan involves a Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. The investments also include $7.5 Billion to implement a nationwide network of 500,000+ EV chargers, as well as an additional $7 Billion to enhance access to minerals and other battery components for US-based vehicle manufacturers (a place-of-assembly restriction).
The IIJA focuses specifically on incentivizing the expansion of the United States’ EV charging infrastructure with the goal of expediting the transition from combustion vehicles to electric vehicles. The act consists of two grant programs: the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula (NEVI) and the Charging and Fueling Infrastructure Grants. Both programs aim to encourage the expansion of publicly accessible EV charging stations nationally and at the state level.
Different Types of Electric Vehicle Service Equipment (EVSE)
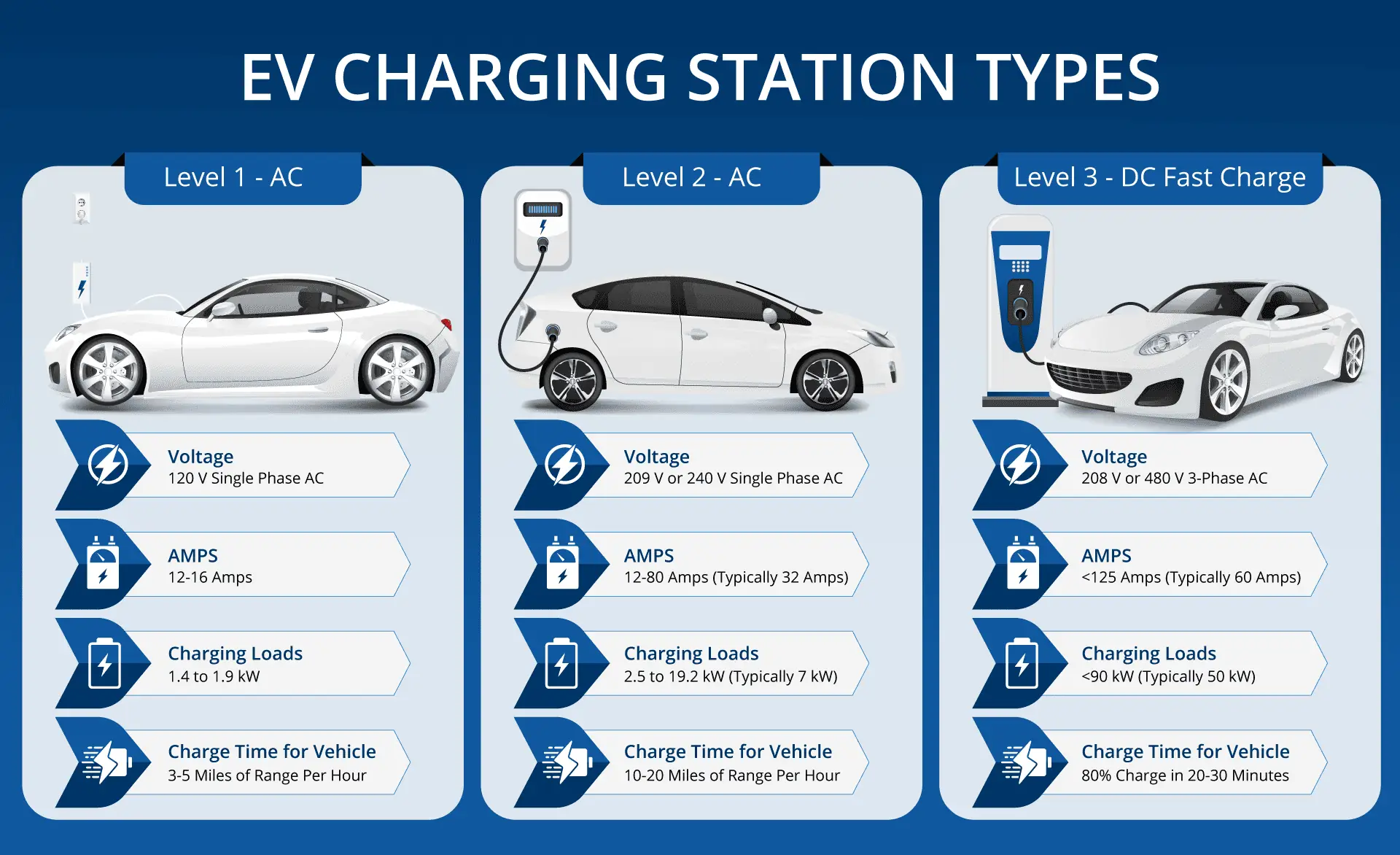
When it comes to charging your EV or fleet of EVs, there are several options. There are three main levels of charging equipment. They are categorized by the different voltage levels and speed at which they charge an electric vehicle.
Level 1
Level 1 charging is typically used in households for overnight charging. These chargers provide 3-5 miles of range per hour and charge through a standard 120 v AC outlet.
Level 2
Level 2 charging is typically used in office buildings, apartment buildings, hotels or for fleets. These chargers are faster than Level 1 and use a 208/240 v outlet. They typically provide 10-20 miles of range per hour. In 2021, 80% of public EVSE ports in the United States were Level 2.
Level 3 or DC Fast Chargers (DCFC)
Level 3 is the fastest level of charging. Level 3 chargers are typically used for commercial or heavy-duty fleets, distribution centers, utilities, transportation companies and highway rest stops. These chargers require a 480 v, three-phase input. Depending on the vehicle, most Level 3 chargers can charge and EV to 80% in 20-30 minutes.
Essential Steps in Fleet Electrification
Here are the critical steps in electrifying fleets and how AWG plays a pivotal role in this endeavor:
1. Establishing Charging Needs and Options
Identifying the particular charging requirements is one of the first steps in fleet electrification. It starts with a detailed understanding of the types of automobiles included in the fleet. Specifically, consider if smaller EVs or larger electric trucks will be utilized, as each vehicle category has different charging requirements. Payload capacity and daily range are also critical factors. For instance, two fleets with daily ranges of 50 mil per vehicle can have different requirements if one is charged with delivering heavy tools.
AWG can help assess these factors and recommend solutions, whether Level 2 chargers for overnight charging or Level 3 DCFCs for rapid charging.
2. Working With Utilities
Collaboration with local utility providers is a critical phase in the infrastructure development process for electrifying fleets. Utility partners align the charging requirements to available electrical capacity and existing infrastructure. Their expertise ensures that the power grid can meet the expected electric fleet charging demands.
AWG can facilitate this communication between businesses and utility providers. Our team excels at ensuring the smooth integration of local services by acting as knowledgeable intermediaries. This approach simplifies the electrification process, helping our clients unlock the full potential of their electric fleet while effectively managing operational costs.
3. Determining Site Locations
A key criterion in site selection is proximity to existing electrical infrastructure, ensuring efficient power distribution to charging stations. Access to a wireless internet connection is also imperative for real-time monitoring and management of the equipment. This connectivity enables companies to track usage, address issues promptly, and optimize their charging operations.
Safety takes precedence in the site selection, involving thorough assessments of potential hazards such as weather-related risks and ensuring convenient access for users. AWG’s expertise in this phase is invaluable, guiding clients to make informed decisions prioritizing safety and operational efficiency.
4. Planning
Effective planning is the cornerstone of a successful transition to an EV fleet. The project plan involves numerous elements, including the following:
- Quantity and types of required charging units
- Strategic placement of equipment for convenient access
- Evaluation of environmental factors
- Accessibility for drivers
- Compliance with state, local, and national regulations
- Permit for inspection processes
- Cost estimation, including potential incentives and ongoing expenses
AWG offers invaluable assistance in crafting a comprehensive project plan tailored to specific needs and budget constraints.
5. Implementing the Plan
During this phase, clear charging policies are established for staff and drivers. This is particularly relevant if multiple parties will be using the infrastructure. Proper training is provided to individuals involved in vehicle charging, including the drivers, fleet operations personnel, technicians, and local first responders. AWG provides resources and guidance to ensure a seamless implementation process.
| At AWG, we strive to increase global sustainability as a material supplier of high-performance cabling systems for the electric vehicle infrastructure. With our complete solutions, our customers are able to deploy an EV charging network efficiently and quickly.
We offer the following cabling options for EV charging infrastructure: ● Grounding Wire ● Low Voltage Cables ● Medium Voltage Cables ● High- and Extra-Voltage Power Cables ● Control Cables ● Fiber Optics Cables ● Transmission & Distribution Wire ● Transformers ● Switchgear ● Panelboards ● Inverters ● Accessories (Electrical Equipment) |
Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Solutions With American Wire Group
AWG supplies high-performance wire and cable solutions for the electric vehicle infrastructure build out.
At AWG, we are enabling the nationwide electric vehicle charging infrastructure expansion. We provide cable system solutions that power charging systems hardware and equipment. Our range of products includes low-voltage cables, medium-voltage cables, control cables, fiber optic cables and equipment such as inverters, transformers, switchgear and electrical equipment for the EV infrastructure.
We work with our customers from design and conception to build the most efficient EV infrastructure network. We offer full lifecycle support, including full project technical support for every project, ensuring that our products meet or exceed performance expectations throughout their entire service life.
AWG support doesn’t end after product completion. Our extensive support and resources are available to assist your company whenever you need them.